Joining Fee By Credit Cards
It is a one-time fee charged by credit cards company for issuing the credit cards. It is usually the annual fee for the 1st year.
Further Reading: What is Mutual Fund
Currently, there are many cards that are offered for free, for example, ICICI Bank Platinum Chip Credit Card, IndusInd Bank Platinum Card and many more.
These cards are issued without any joining fee as well as without any renewal fee.
Annual fee/ Renewal Fee –
It is a fee levied by the credit card company on the card holder for using credit card. This annual fee is billed to your next monthly statement after the end of the first year. However, not all credit cards charge this fee while some of the credit card issuers waive off this annual fee if the customer uses his/her credit for purchases beyond a certain limit, for example, SBI SimplyCLICK credit card waives of annual fee of the subsequent year upon spending Rs. 1 lac in the current year..
Statements
Statements will be issued once every month to the card holder. Generally, e-statements are sent, however, there is an option of requesting paper statements which is chargeable. No statement will be issued in case the balance is below 100 (this limit could be different in case of other cards).
The date on which statement is generated is known as Statement Date and the date by which the outstanding balance is payable is known as Payment Due Date.
Billing Cycle
Billing cycle is the interval or period from the end of one billing statement date to the next statement date. Billing cycle is not standardized in the sense that it is dependent on the date of issuance of the credit card and hence may vary for different credit cardholders. The date on which the first statement is generated will remain the same for the subsequent statements irrespective of the days in any month. For instance, your first statement is generated on 2nd Jan. So every subsequent statement will be generated on 2nd of every month only.
Interest free (Grace) period –
It is the period for which you use the credit, without paying any interest on it. This period can vary from 20-50 days or even more depending on the credit card issuer. The interest-free period does not apply for cash advances and revolving balances.
For example, suppose your statement date is 17th November covering transactions between 18th October to 17th November and payment due date is 5th December. In this case, payment due date is 18 days after the statement date. So, if you have made a transaction on 18th October then interest-free period is 48 days (18 Oct – 5 Dec) whereas, for a transaction made on 17th November, the interest-free period is only 18 days (17 Nov – 5 Dec).
Also Read: What is National Pension Scheme? A complete overview !
Annualized Percentage Rate –
The monthly interest rate charged by the credit card company when annualized gives APR (Annualized Percentage Rate). Monthly interest rate of 4% p.m. will translate into 48% APR.
Minimum Amount Due –
It is the amount to be paid to the bank/credit card company before the due date in order to avoid any penalty or late fees imposed by the issuer of the credit card. Minimum amount due is usually higher of the following: –
a) 5% of total outstanding plus ongoing EMI plus taxes if any
b) Minimum amount as specified by the card issuer (for example in case SBI and HDFC cards it is Rs. 200)
Any unpaid Minimum Amount Due of the previous statements will be carried forward in the next statement and will be added in the next statement’s Minimum Amount Due.
Customers should not make a habit of paying only minimum amount because interest will be levied on the rest outstanding amount. For instance, on 15th April you spend Rs. 5,000 by using your credit card and your statement is generated on 15th May with a payment due date of 1st June. So, by 1st June you should pay your bill of Rs. 5,000 to the credit card company. Credit card companies will also give you an option of paying only a minimum amount. But customers should avoid falling for this, as it only prevents you from paying late fee but not the interest that will be charged on the credit availed by you. So always pay your credit card bills in time when you have the money.
Credit Limit –
This is the maximum amount up to which you can use your credit card for purchases. The assignment of credit limit is at the sole discretion of the credit card company. The credit limit can be increased or decreased based on your usage and repayments of bills. If you pay your credit card bills irregularly or fully utilize your credit limit every month then credit card issuer might decrease your credit limit.
Available Credit Limit
It is the actual amount that is available to the cardholder for spending. Available credit limit is calculated as below: –
Available credit limit = Credit Limit – Current Payable Balance
Cash Limit
Cash limit is the maximum cash one can withdraw using his/her credit card. Withdrawn amount will be subject to fees and charges as applicable. This cash limit is inclusive of the overall credit limit.
Total Payment Dues
It is the total outstanding balance to be payable by the card holder before payment due date. These are calculated as below: –
Previous Balance – Payments – Credits + Finance Charges + Cash Advance = Total Payment Dues
Payment/ Credits
It is the amount received towards your credit card account. It includes payments made by the cardholder towards his/her credit card account, cash back, etc.
Purchases/ Debits
It is the total amount of transactions charged towards your credit card account. Simply put, it is the total amount you spend using your credit card account.
Opening Balance
It is the closing balance of the previous statement. For example, if the total payment dues are 2,000 as per your previous statement then in the current statement it will be shown as opening balance.
Finance Charges
Finance charges are payable on all transactions including EMI from the date of transaction if the cardholder does not pay his/her balance in full and as well as on all cash advances taken by cardholder.
| Option | How interest will be levied |
| 1) If full payment of Total Outstanding is made before Payment Due Date | No interest will be levied |
| 2) If partial payment is made before Payment Due Date | Interest will be charged for all transactions made in the current cycle from the date of transactionThe closing balance will attract interest from one day post the Statement Date till one day prior to the payment date |
| 3) If you usually make Partial payment, but in the Current month you have settled your Outstanding dues in full before Payment date | Only the closing balance as per your previous will accrue interest until the payment date |
Following are the examples of the above cases –
- Example of Option 1
Statement date – 1st Oct
Payment due date – 21st Oct
Payment Made – Up to or on 21st Oct
Note: – The payment should be realized by the credit card company before the payment due date. For example, if you make the payment through cheque then take care of the fact that the payment gets realized by the credit card issuing company on or before payment due date.
- Example of Option 2
1st Oct – Statement Generated with previous outstanding balance of Rs. 15,000 and with the Payment Due Date of 21st Oct.
10th Oct – Transaction made for Rs. 3,000
21st Oct – Payment of Rs. 10,000 made to the credit card company
1st Nov – New statement will be generated with previous outstanding balance of Rs. 8,000 along with interest charges for the following:-
- Interest on Rs. 15,000 from 2nd Oct to 20th Oct
- Interest on Rs. 5,000 (15000-10000) from 21st Oct to 1st Nov
- Interest on Rs. 3,000 from 10th Oct to 1st Nov
- Example of Option 3
1st Oct – Statement Generated with previous outstanding balance of Rs. 15,000 and with the Payment Due Date of 21st Oct.
19th Oct – Payment of Rs. 15,000 made to the credit card company
1st Nov – New Statement will be generated with interest on Rs 15,000 from 2nd Oct to 18th Oct i.e. for 17 days
Further Reading: Mutual Funds Sahi Hai
Late Payment Charges
Credit card companies impose late payment charges if the cardholder does not pay Minimum Amount Due before Payment Due Date. These charges generally vary from bank to bank. Following are the late payment charges of HDFC bank: –
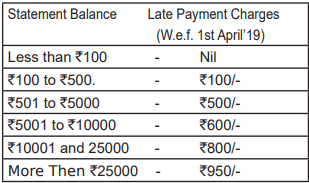
Some credit card companies impose late fee charges over and above these charges.
Cash Advances
Cardholders can make use of their credit cards to access cash in case of emergency from any domestic/international ATMs. A transaction fee would be levied on all such withdrawals which would be higher of 2.5% or Rs. 500. This transaction fee would be billed to the cardholder in the next statement. Finance charges are to be paid on cash advances from the date of transaction over and above cash advance fee.
Other Charges charged by the credit card companies
- Cheque Bounce Charges
In case the cheque deposited towards bill payment bounces for whatever reason, then credit card company will impose cheque bounce charges.
- Over Limit Charges
These charges are applicable on total outstanding amount exceeding credit limit at a rate of 2.5% or 500 whichever is higher.
- Reward Handling Charges
Some credit card issuing companies impose reward handling charges on the cardholder. A fee of around Rs. 99 + GST is levied on every redemption request.
- Cash Repayment Fee
Cardholders can make payments towards their outstanding dues by depositing cash at any nearby branch of the credit card issuing bank. Some credit card issuing companies do not accept cash.Example: American Express.
- Card Replacement Charges
Some credit card companies charge a flat fee for reissuing/replacement of card. For example, SBI levies a flat fee of Rs. 100 for card replacement. But when a card is replaced due to any compliance then this fee is not imposed on the cardholders.
- Overseas Transactions
Credit card companies levy a transaction fee on all overseas transactions which is generally 3.5% of transaction value. For instance, you spend 100 Pounds with any foreign merchant and the current rate of conversion is 1 Pound = 90 INR then a transaction fee of 3.5% will be levied on Rs. 9,000 (100×90) i.e. 315.
- Cheque/Cash Pick Up fee
Cardholders can request for cheque/cash pick up but a flat fee is usually charged. For example, ICICI Bank charges Rs. 100 per pick-up.
Note: – All these charges may vary from bank to bank. Also, GST (Goods and Services Tax) will be levied on all taxable supplies (fees or charges) at applicable rates.
Also Read:
Surcharges
Surcharges are imposed on railway transactions as well as on petrol transactions. These charges also vary across different credit cards. Some credit cards come with a waiver of surcharge. For example, IndianOil Citi Platinum Credit Card provides full waiver of fuel surcharge on any bank’s EDC machine. IRCTC SBI Platinum Card is an exception that waives of transaction charges on railway ticket booking.
Add on cards
Add on cards, also known as supplementary cards can be issued to the family members of the primary cardholders upon request. These cards are usually issued free of cost. For example, SBI issues a maximum of two add on cards for every eligible primary card.
No extra credit limit is offered on this add on card as it has to be shared with the credit limit of the primary holder. Even though the card is issued to other family members, but the primary cardholder is liable for payment of charges and all transactions made from these cards.
Rewards
Credit cardholders get rewarded for every rupee they spend. Credit card issuing companies reward customers to encourage spending. These rewards can be in the form of points or miles or vouchers.
Cash back
Certain online shopping websites come up with instant discounts or offer cashbacks on specific credit cards from time to time. By holding multiple credit cards of different companies you may increase your chances of grabbing these offers.
Customers Liability in case of loss/theft/misuse of card
- In case of loss/misuse/theft
Card holder is responsible for any transactions incurred on the card account prior to reporting of loss.
- In case of fraudulent transactions
RBI has passed regulations in order to limit cardholder’s liability.
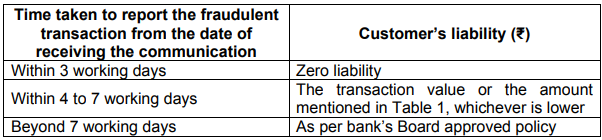
Overall liability as per RBI for fraudulent transactions: –
- Credit card with limit up to 5 lakhs – Max Liability of the customer is Rs.10,000
- Credit card with limit above 5 lakhs – Max Liability of the customer is Rs.25,000
Death or Insolvency of a Cardholder
The entire outstanding dues shall become payable in full by the cardholder’s family in the event of his death or in case of insolvency.
Revocation/Termination of Cardholder
Cardholder may at anytime revoke or end the Agreement. Credit card issuing company can also terminate or suspend the use of credit card at any time before any prior notice.
In both the cases the cardholder must pay all outstanding dues immediately.
Further Reading: HDFC Bank

